Glossary
Some concepts and definitions in Clusternet
Definitions
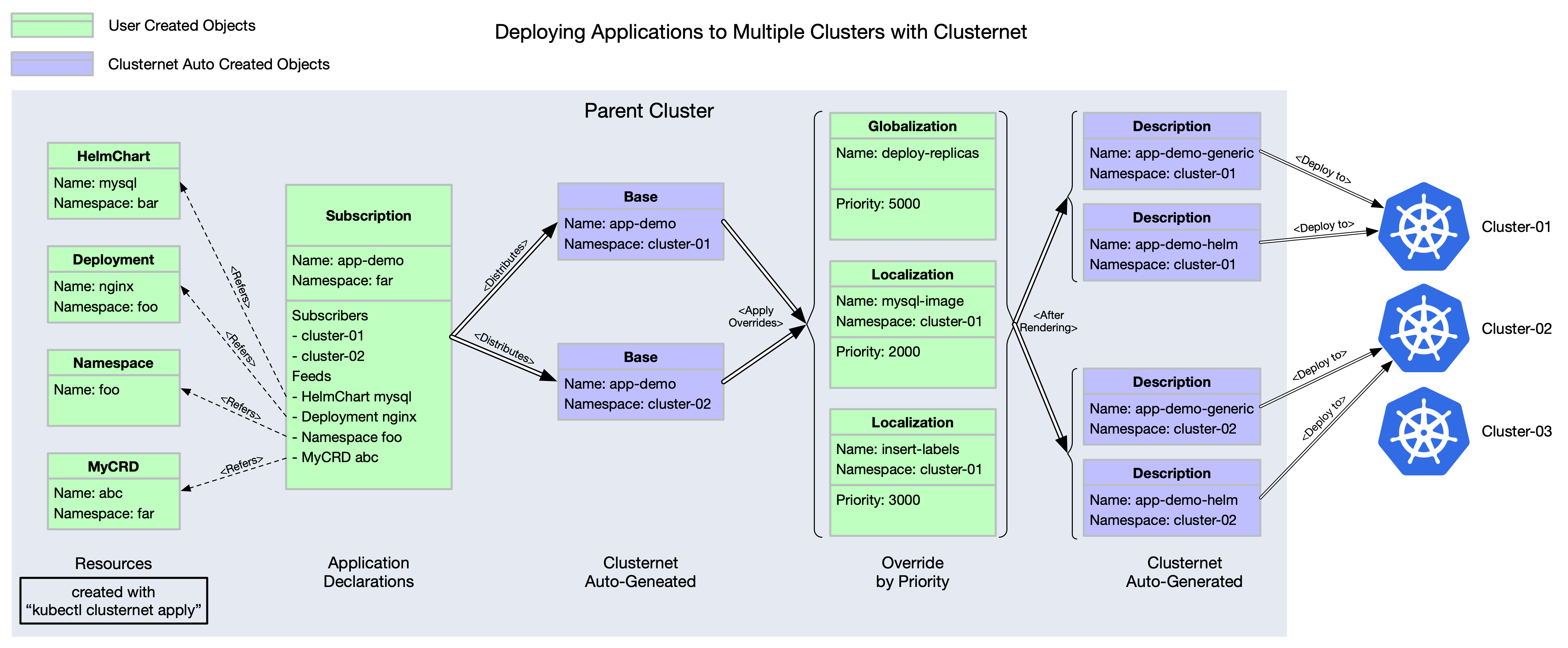
For every Kubernetes cluster that wants to be managed, we call it child cluster. The cluster where child clusters are registerring to, we call it parent cluster.
clusternet-agent runs in child cluster, while clusternet-scheduler
and clusternet-hub runs in parent cluster.
CRDs
ClusterRegistrationRequestis an object thatclusternet-agentcreates in parent cluster for child cluster registration.ManagedClusteris an object thatclusternet-hubcreates in parent cluster after approvingClusterRegistrationRequest.HelmChartis an object contains a helm chart configuration.Subscriptiondefines the resources (we call them as a group ofFeeds) that subscribers want to install into clusters. VariousSchedulingStrategyare supported, such asReplication,StaticDividingandDynamicDividing. For every matched cluster, a correspondingBaseobject will be created in its dedicated namespace.Clusternetprovides a two-stage priority based override strategy.LocalizationandGlobalizationwill define the overrides with priority, where lower numbers are considered lower priority.Localizationis namespace-scoped resource, whileGlobalizationis cluster-scoped. Refer to tutorial on how to set overrides in Clusternet.Baseobjects will be rendered toDescriptionobjects withGlobalizationandLocalizationsettings applied.Descriptionis the final resources to be deployed into target child clusters.FeedInventoryobjects are used to track and record the scheduling requirements (such as replicas, node selectors, tolerations, affinity rules, resource requirements, etc.) for each feed in theSubscriptionobject of the same name. ThisFeedInventoryobject is only applicable whenSchedulingStrategyis set toDynamicDividing. For other scheduling strategies,FeedInventorymakes no sense.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.
Last modified June 2, 2023: add doc on feed inventory (#86) (db1bc3b)